Contact for the resource
University of Cagliari/EvK2CNR
2 record(s)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
Status
Scale
-
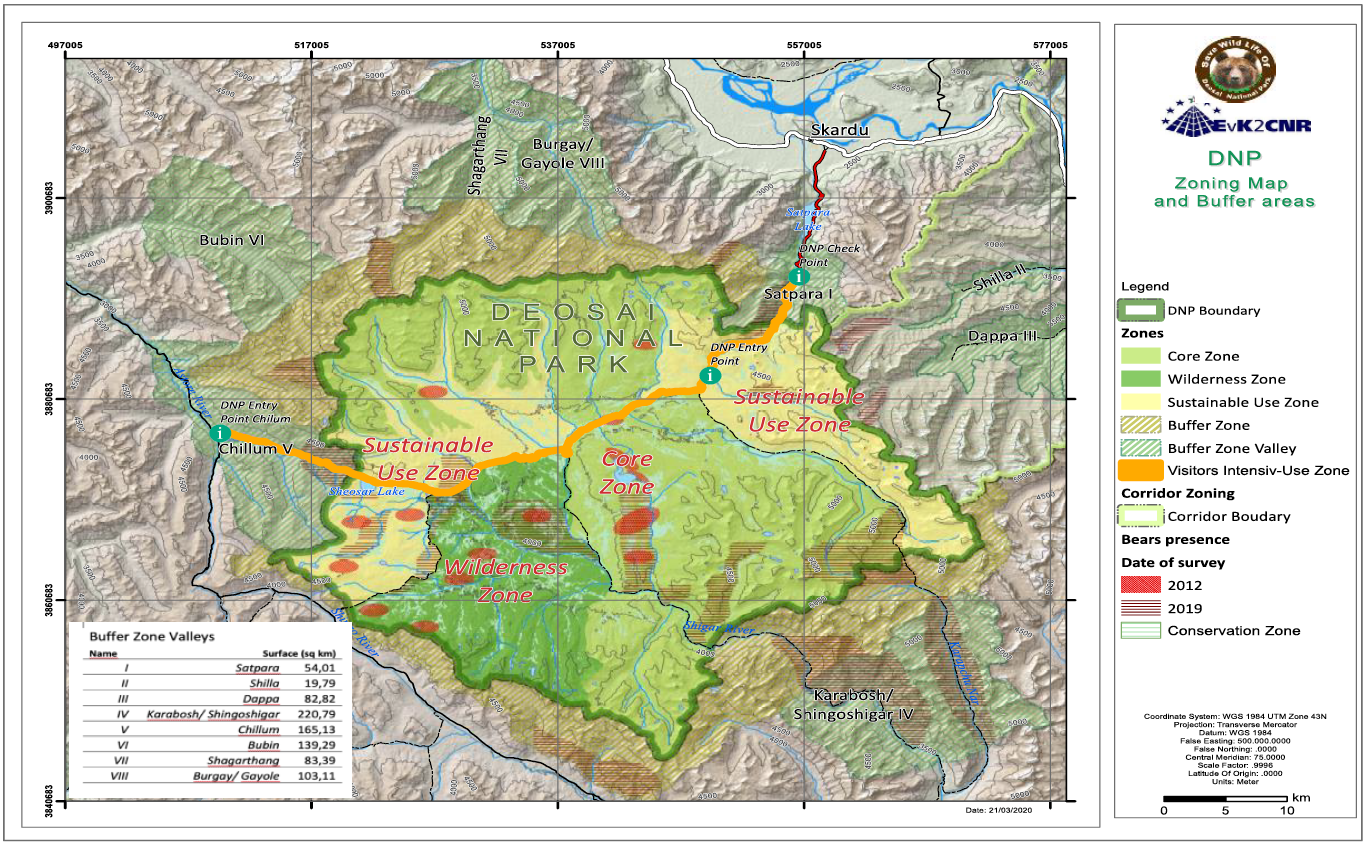
The zoning exercise conducted for DNP aimed to balance use and conservation, keeping conservation as a priority; however, without compromising the sustainable use of the Park. The use includes that allowed under the legislation, namely recreation and education, and traditional rights of the local communities and the Gujjar-Bakarwals that are dependent on the DNP. The Deosai National Park is designated as “National Park” under the wildlife legislation. However, to allow for development of tailored management principles for different areas within the DNP designated zones, their purpose, and broad management guidelines are described in this chapter: there are four different zones inside the Park Boundaries and two zones outside the park in a comprehensive Buffer Zone. • Core Zone • Wilderness Zone • Sustainable Use Zone • Visitors Intensive-Use Zone Outside the Park boundaries: • Buffer Zone • Buffer Zone Valleys
-
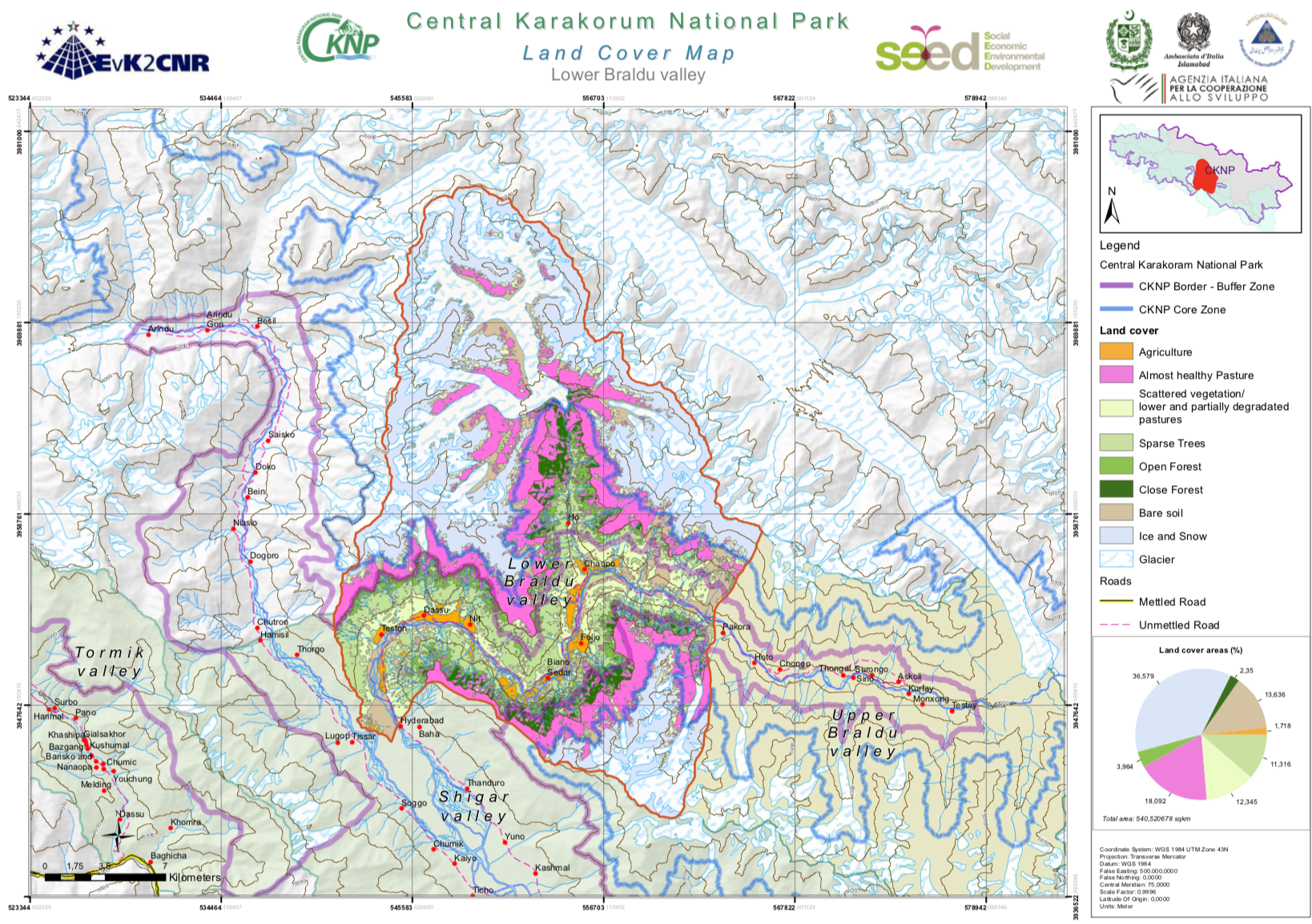
The Central Karakorum National Park (CKNP) is one of the most important national parks of Pakistan and comprises one of the largest mountain glacial systems in the world with Siachen (75 km), Baltoro (57 km) and Hispar-Biafo (122 km) glaciers originating within its boundaries. Administratively, it is situated in the Skardu and Gilgit districts of the Gilgit and Baltistan Region of Pakistan. The 72,500 km2 national park borders China, Afghanistan, and India, and represents one section of the of Hindu Kush-Karakorum-Himalaya mountain range. The area is part of the "transitional zone" between the arid Central Asia and the semi-humid subtropics of the northern South Asia. The land cover map for the CKNP has been divided into 14 subregions as follows: - Astak - Bagrot - Basha - Daghoni - Danyore - Ghulmat - Haramosh - Hopper - Lower Braldu - Nagar - Shigar - Thalay - Tormik - Upper Braldu
